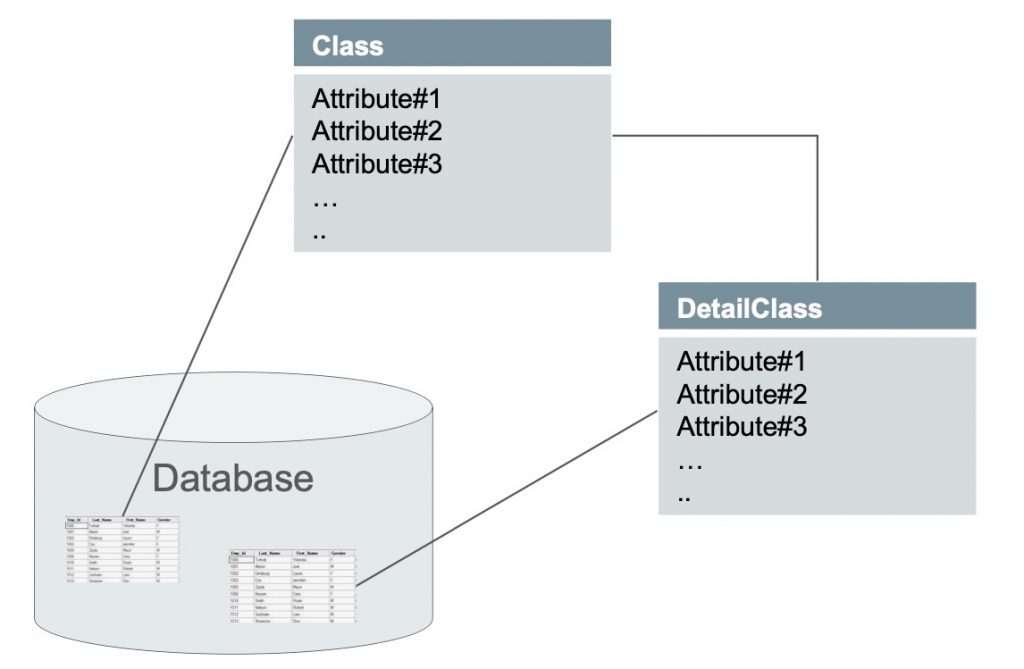
Class Attributes
Class attributes are the fields that provide context. When classes are saved in the database, each class is represented as a table in the database, and attributes as columns of the database table for the class.
Conventions and Rules for Attribute Names
Since attributes are represented as columns in the database table for the class, the following rules and conventions are for naming attributes are followed.
- No spaces allowed
- Maximum number of characters is 32
- Use CamelCase Notation as a convention to take advantage of automated rendering when displaying the form
- Names cannot start with numbers
- Avoid special characters
Attribute Properties
Several attribute properties are set when creating and changing class attribute definitions.
name
Name of the attribute. Since attributes are represented as columns in the database table for the class, the following rules and conventions for naming attributes are followed.
- No spaces allowed
- The maximum number of characters is 32
- Use CamelCase Notation as a convention to take advantage of automated rendering when displaying the form
- Names cannot start with numbers
- Avoid special characters
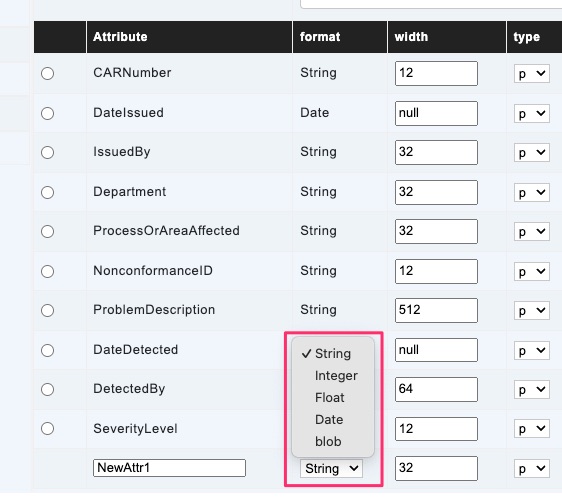
format
The most essential property aside from the name is the attribute’s format.
The five available types are String, Integer, Float, Date, and blob.
width
The width property is applicable and used when the attribute’s format is String. For example, a value of 12 for width (String format) means up to 12 characters can be saved in the field. As for the database column, 12 translates to VARCHAR(12).
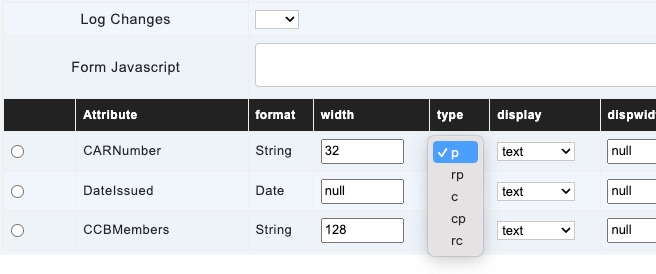
type
The type property indicates the persistence behavior of the attribute
- p – Attribute is persisted in the database
- rp – Attribute is required and persisted in the database
- c – Attribute is calculated and not persisted in the database
- cp – Attribute is calculated and persisted in the database
- rc – Attribute is required and calculated
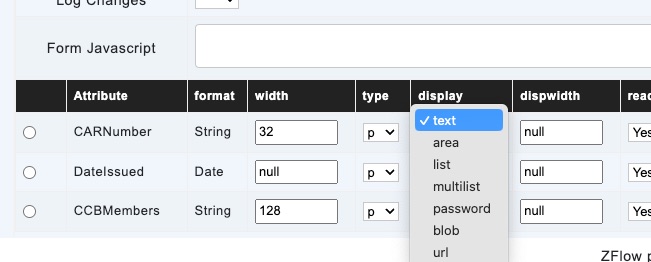
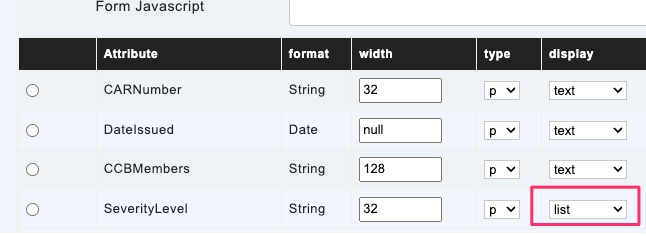
display
Display property allows how the value of an Attribute is handled on the form.
- text – Attribute is displayed as text field
- area – Attribute is displayed as area
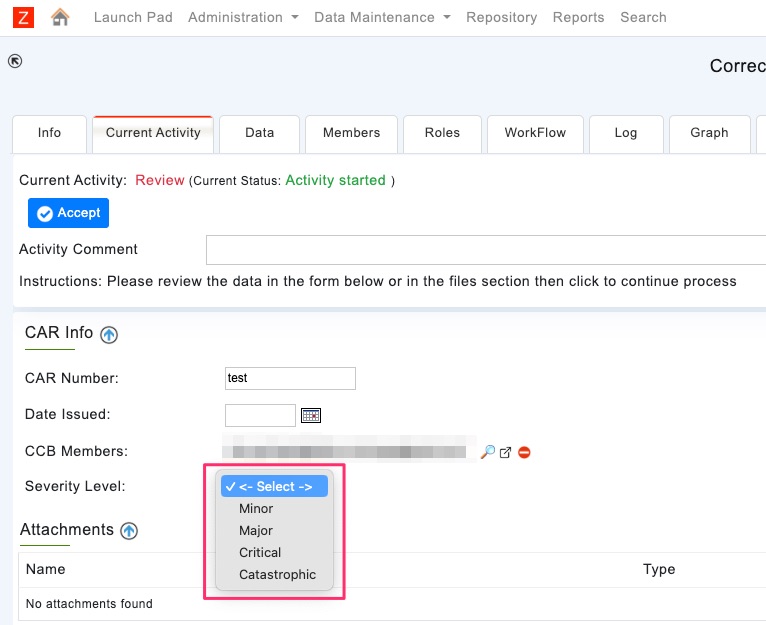
- list – Attribute is displayed as a value from drop-down list
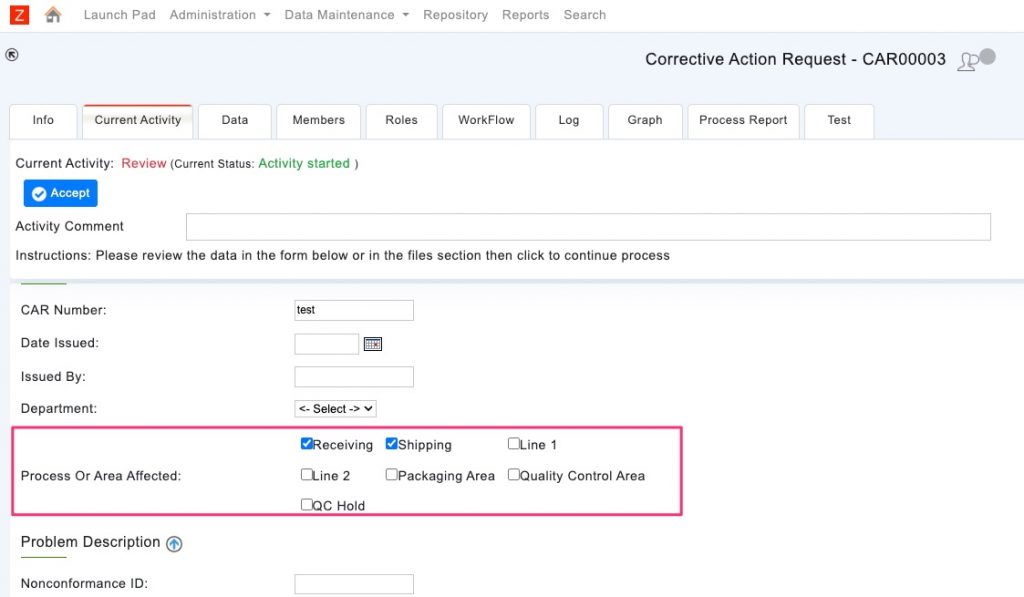
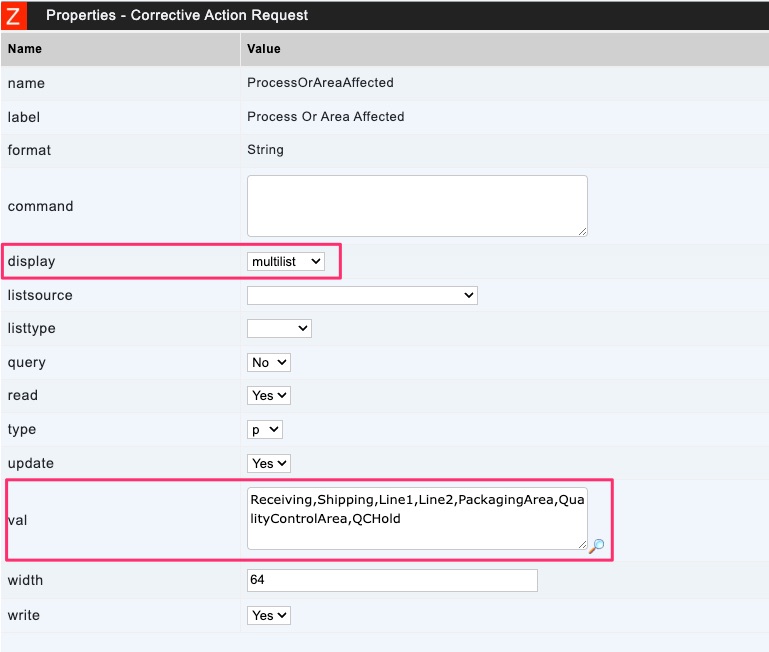
- multilist – Attribute is displayed as selectable items with checkboxes
- password – Attribute is displayed as a password field (value is not visible)
- blob– Attribute is downloadable file
- url – Rendered as clickable URL link
dispwidth
This property is applicable when the display property is set to text. The dispwidth is the width of the field on the form.
read
This property controls the visibility of the attribute (Yes means it is visible in the form; No means the attribute is not visible in the form)
write
This property controls the visibility of the attribute when the process/object is being created. (Yes means it is visible in the form; No means the attribute is not visible in the form)
update
This property controls the attribute’s visibility when the process/object is updated. (Yes means it is editable; No means it is not editable)
query
This property controls if the attribute can be used for query (as criteria) when searching. (Yes means it is used; No means it is not used)
The following properties are applicable when the display property value is list
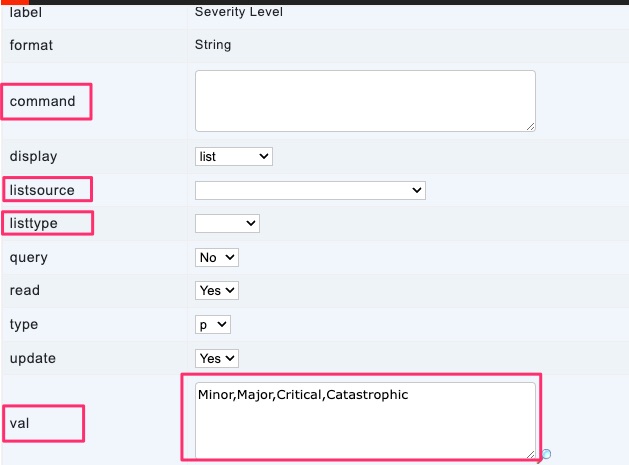
val
Comma separated values that are in the val property become list options
listtype
listtype property can be derived (most common), actual, or config
listsource
listtype property can be query (most common), program, or class
command
command property is the SQL query that will be used in conjunction with derived and query to generate the list of options for drop-down lists
default
default property when set adds the value as the default when an object is created
min
minimum accepted value (applicable when format is Float or Integer)
max
maximum accepted value (applicable when format is Float or Integer)
units
helpful text to indicate the unit of value
help
help text that is displayed when the cursor hovers over the field
select
Allows selection of attribute value of another object by searching and selecting
selcrit
Works in conjunction with Property that restricts the search to list the objects to meet the criteria
dispformat
Property for showing attribute values in a specific format (applicable for Date, Float). Examples below
- Date – yyyy/MM/dd
- Float – #,###,##0.00
Examples
Multilist
Attribute Properties
List (with values)
List (using query)
Text (using select)
Text (Display Area)
Drop-down value selected is TransportationGroup from table TTGRT. Description from table TTGRT is displayed on the screen
display – list
listsource – query
listtype – derived
command – select TransportationGroup,’::’,Description from TTGRT
Date Examples
default=“TIME.Date” dispformat=“yyyy/MM/dd” display=“text” dispwidth=“10” format=“Date”
List Examples
command=“select Email,’::’,LastName,’ ‘,FirstName from Usr where Role=’Assistant'” display=“list” listsource=“query” listtype=“derived”
command=“select Email,’::’,CONCAT(FirstName,’ ‘,LastName) from Usr where Role = ‘Customer’ order by FirstName,LastName” multiselect=“Usr:EMail:FirstName,LastName:autocomplete” selcrit=“Role = ‘Customer'”
select Value,’::’,CONCAT(Value,’-‘,Description) from Family where Organization=’__Organization__’ order by Value asc
command=“select Email,’::’,LastName,’ ‘,FirstName from Usr where Role=’Assistant'” display=“list” listsource=“query” listtype=“derived”
command=“Select CompanyCode from CompanyCode order by CompanyCode asc” display=“list” listsource=“query” listtype=“derived”
trans=“name:Collaboration” listtype=“derived” listsource=“query” command=“select UID,’::’,CID from Collaboration where UID = ‘__CollabID__‘ order by CollID” copy=“-“ view=“Collaboration:UID” val=‘::None’/>
Multilist Examples
display=“multilist” admin_update=“+” dispwidth=“5” listtype=“derived” listsource=“com.*.*.*” command=“get*********”/>
Select Examples
Multiselect Examples
command="select Email,'::',CONCAT(FirstName,' ',LastName) from Usr where Role = 'Customer' order by FirstName,LastName" display="text" multiselect="Usr:EMail:FirstName,LastName:autocomplete" selcrit="Role = 'Customer'"
Float Examples
Integer Examples
String Examples
Javascript Function Examples
<Attr name=”SupplierID” display=”text” format=”String” nonchangeable=”+” query=”+” read=”+” type=”rp” update=”+” width=”64″ write=”+” jsfunc=”isUnique(this, ‘Supplier’, ‘SupplierID’)”/>