ZFlow can be easily installed on AWS Linux using the instructions below. We assume that your organization or you have an AWS account and are familiar with AWS services, particularly EC2.
Launching AWS Linux Instance
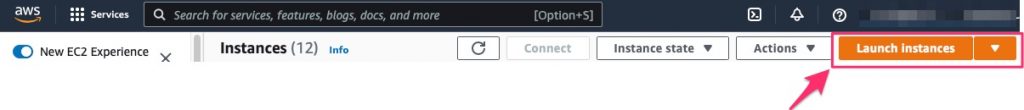
The first step is to log in to your AWS account and navigate to the EC2 Dashboard from the console panel. Create an AWS Linux 2023 using “Launch Instances”
Refer to the AWS documentation for additional guidance on launching AWS Linux instances.
Install Java
Once you can access the above AWS instance using SSH, you can start the process of installing prerequisites. If you are new to EC2, you can learn more about how to access EC2 instances using SSH in the following AWS user guide.
AWS Corretto
Use the command below to install AWS’s distribution of OpenJDK
sudo yum install java-17-amazon-corretto
(or)
sudo dnf install -y java-17-amazon-corretto
You can check Java version using the following command
java -version
You should see something like below
openjdk version "21.0.3" 2024-04-16 LTS
OpenJDK Runtime Environment Corretto-21.0.3.9.1 (build 21.0.3+9-LTS)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM Corretto-21.0.3.9.1 (build 21.0.3+9-LTS, mixed mode, sharing)
Install Tomcat
You can install Tomcat 9 using the following command
sudo yum install tomcat9
You can start tomcat9 service with the following commands
sudo systemctl start tomcat9 (or) sudo service tomcat9 start
You can stop tomcat9 service with the following commands
sudo systemctl stop tomcat9 (or) sudo service tomcat9 stop
You can use the following command to enable Tomcat to start automatically when the server boots up
sudo systemctl enable tomcat9
You can look at the tomcat log using the following command
journalctl -f -u tomcat9
The webapps directory of tomcat is located under
/var/lib/tomcat9
Install MySQL8
You can use instructions in the below link to install MySQL community server in the AWS instance you just created.
Since AWS Linux does not have MySQL repositories the first step is to add the source repo using the command below
sudo rpm -Uvh https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el9-1.noarch.rpm
Once the repo is installed use the command below to install MySQL community server
sudo yum install mysql-community-server
To set MySQL server to start on boot using the following command
sudo systemctl enable mysqld
Start MySQL server using the command below
sudo systemctl start mysqld
By default MySQL 5.7 installation generates a temporary password. To find the password use the following command
sudo grep "password" /var/log/mysqld.log
Take a note of the above password since you will use that password in the step below.
Use the following command to reset the password and secure the installation.
sudo mysql_secure_installation
Remember the new password as you will need it in the next step. Learn more about MySQL Secure Installation.
Once MySQL is up and running the first step is to create a database user and database for zflow. You can login as MySQL root user to create the user and database with the following commands
mysql -u root -p
Creating Database and Database user for ZFlow in MySQL (when MySQL is running on the same server that ZFlow is running)
Once connected to MySQL, create the user with the following command. Come up with appropriate names for the following for your ZFlow installation, and keep them handy
- userforzflowdatabase
- password_for_zflowdbuser
- databaseforzflow
mysql> CREATE USER 'userforzflowdatabase'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password_for_zflowdbuser';
Make sure you give appropriate username and password in the above command and remember these as you will need them for configuring ZFlow.
mysql> CREATE DATABASE databaseforzflow; mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON databaseforzflow.* TO 'userforzflowdatabase'@'localhost'; mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
AWS RDS MySQL Databases
For RDS Systems (or scenarios where the MySQL server is different from the one where ZFlow is running), the user is created as follows. Please replace the user and database names with your values.
mysql> CREATE USER 'userforzflowdatabase'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password_for_zflowdbuser'; mysql> CREATE DATABASE databaseforzflow; mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON databaseforzflow.* TO 'userforzflowdatabase'@'%'; mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Install ZFlow
Go to the home directory of ec2-user and download ZFlow with the commands below
[ec2-user@ip-******** ~]$ cd $HOME
Please send us an email or contact us for ZFlow distribution. ZFlow distribution is a tar file (zflow.tar.gz) that you can unzip and untar using the commands below
[ec2-user@ip-******** ~]$ gunzip zflow.tar.gz [ec2-user@ip-******** ~]$ tar -xvf zflow.tar
You should have the zflow directory with related application files listed
[ec2-user@ip-******** ~]$ ls working zflow
Move zflow directory to the webapps directory
[ec2-user@ip-******** ~]$ sudo mv zflow /var/lib/tomcat/webapps/
Change directory to webapps folder
[ec2-user@ip-******** ~]$ cd /var/lib/tomcat/webapps/
Change group and user ownership of zflow to tomcat
[ec2-user@ip-******** ~]$ sudo chown -R tomcat:tomcat zflow
ZFlow Configuration Properties
Once this step is finished you can go back to the home directory and start tomcat server
sudo systemctl start tomcat